Yo, check it – stock portfolio analysis is where it’s at for savvy investors looking to level up their game. Get ready to explore the ins and outs of this crucial tool that can make or break your investment decisions.
So buckle up and let’s dive into the exciting world of stock portfolio analysis.
Importance of Stock Portfolio Analysis
Stock portfolio analysis is crucial for investors as it allows them to track the performance of their investments, identify trends, and make informed decisions to maximize returns and minimize risks.
Understanding Market Trends
Regularly analyzing a stock portfolio can help investors understand market trends and adjust their investment strategies accordingly. For example, by noticing a consistent increase in the value of technology stocks, investors may decide to allocate more funds towards this sector to capitalize on the trend.
Risk Management
Analyzing a stock portfolio also helps in risk management by diversifying investments across different asset classes. By spreading investments in various industries or geographic regions, investors can reduce the impact of a downturn in a specific sector on their overall portfolio.
Performance Evaluation
Another benefit of regularly reviewing and analyzing a stock portfolio is evaluating the performance of individual stocks. By comparing the performance of each stock against relevant benchmarks, investors can identify underperforming assets and decide whether to hold, sell, or buy more shares.
Types of Stock Portfolio Analysis
When it comes to analyzing a stock portfolio, there are several methods that investors can use to gain insights into their investments. Three common types of stock portfolio analysis include fundamental analysis, technical analysis, and quantitative analysis. Each approach offers a unique perspective on the performance and potential of a stock portfolio.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating a stock based on its financial statements, earnings, revenue, and other key metrics. Investors using this method focus on the underlying value of a company and its growth prospects. By analyzing financial data and economic indicators, fundamental analysis can provide insights into the intrinsic value of a stock and help investors make informed decisions.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis, on the other hand, relies on historical price data and trading volume to forecast future price movements. This approach involves studying charts, patterns, and indicators to identify trends and patterns in stock prices. Technical analysts believe that past price movements can help predict future price movements, allowing investors to make trading decisions based on market trends.
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis involves using mathematical models and statistical techniques to evaluate stock performance. This approach focuses on data-driven analysis, such as ratios, algorithms, and mathematical calculations, to assess the risk and return of a stock portfolio. By quantifying market data and trends, quantitative analysis can provide investors with a systematic and objective way to measure the performance of their investments.
Overall, each type of stock portfolio analysis offers a different perspective on evaluating investments. Fundamental analysis looks at the intrinsic value of a company, technical analysis focuses on price trends, and quantitative analysis uses data-driven models to assess risk and return. By incorporating these different approaches, investors can gain a comprehensive understanding of their stock portfolio and make informed decisions to maximize their investment opportunities.
Key Metrics and Indicators for Stock Portfolio Analysis
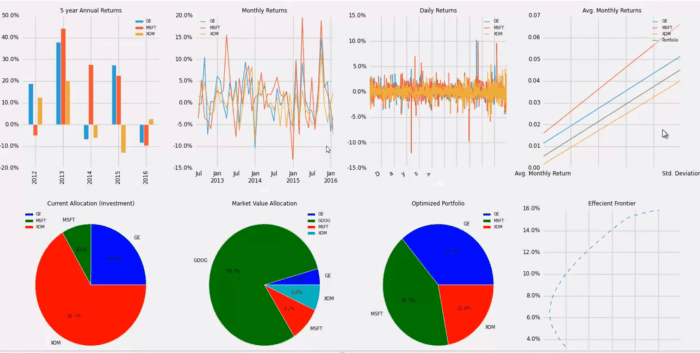
When analyzing a stock portfolio, it is crucial to consider key metrics and indicators that provide insights into the performance and risk associated with the investments. These metrics help investors make informed decisions and assess the overall health of their portfolio.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Return on Investment (ROI) is a fundamental metric used in stock portfolio analysis to measure the profitability of an investment relative to its cost. It is calculated by dividing the net profit from an investment by the initial investment cost and expressing it as a percentage. The formula for ROI is:
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100
A higher ROI indicates a more profitable investment, while a lower ROI suggests lower returns relative to the initial investment.
Risk-Adjusted Return
Risk-Adjusted Return is a metric that takes into account the level of risk associated with an investment when evaluating its return. It helps investors assess whether the returns generated are sufficient given the level of risk taken. One common measure of risk-adjusted return is the Sharpe Ratio, which considers the risk-free rate of return in addition to the investment’s volatility.
Beta
Beta measures the volatility of a stock relative to the overall market. A beta of 1 indicates that the stock’s price moves in line with the market, while a beta greater than 1 suggests higher volatility and a beta less than 1 indicates lower volatility. Investors use beta to assess the risk of a stock compared to the broader market.
Alpha
Alpha measures the excess return generated by an investment compared to its expected return based on its beta. A positive alpha indicates that the investment outperformed its expected return, while a negative alpha suggests underperformance. Alpha is used to evaluate the skill of a portfolio manager in generating returns above or below the market benchmark.
| Metrics and Indicators | Significance |
|---|---|
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Measures profitability relative to cost of investment |
| Risk-Adjusted Return | Accounts for risk in evaluating investment returns |
| Beta | Indicates volatility of a stock relative to the market |
| Alpha | Measures excess return compared to expected return based on beta |
Tools and Software for Stock Portfolio Analysis
Stock portfolio analysis is crucial for investors to make informed decisions and maximize returns. Various tools and software are available in the market to assist investors in analyzing their stock portfolios effectively.
Bloomberg Terminal
Bloomberg Terminal is a popular tool used by professionals for stock portfolio analysis. It provides real-time financial data, market news, and analysis tools to help investors make informed decisions. Key features include financial modeling, charting, and news alerts.
Morningstar
Morningstar is another widely used platform for stock portfolio analysis. It offers detailed research reports, stock ratings, and portfolio tracking tools. Investors can access Morningstar’s extensive database to evaluate the performance and risk of their investments.
Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance is a free platform that provides a wide range of tools for stock portfolio analysis. Users can track their portfolios, view stock quotes, and analyze historical data. Yahoo Finance also offers market news and insights to help investors stay informed.
Comparison Table
| Tool | Key Features | Subscription |
|---|---|---|
| Bloomberg Terminal | Real-time financial data, financial modeling, news alerts | Subscription-based |
| Morningstar | Detailed research reports, stock ratings, portfolio tracking | Subscription-based |
| Yahoo Finance | Portfolio tracking, stock quotes, historical data | Free |
