With investing in REITs at the forefront, get ready to dive into the world of real estate investment trusts like never before. Buckle up as we explore the different types, benefits, risks, and strategies associated with REIT investments in this rollercoaster ride of financial knowledge.
Let’s break down the nitty-gritty details of REIT investing and uncover the secrets to maximizing returns while minimizing risks.
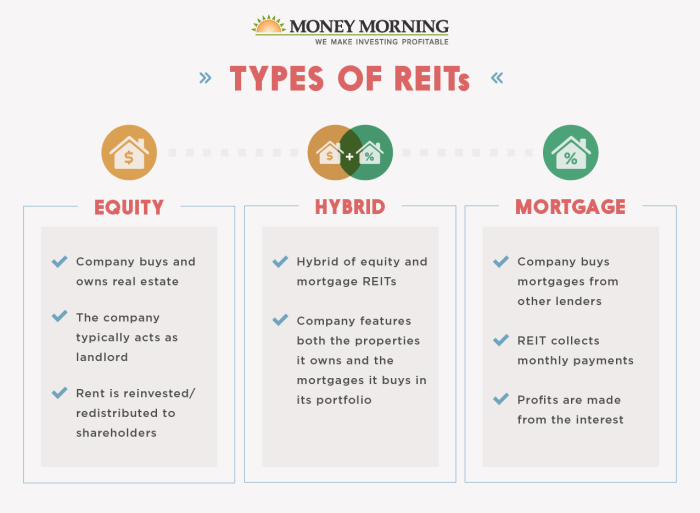
Types of REITs
When it comes to investing in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), there are several types to choose from, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. Let’s take a closer look at the different types of REITs available for investment.
Equity REITs
Equity REITs are the most common type of REITs and invest in and own income-producing real estate. These properties can include office buildings, shopping centers, apartments, and more. The primary source of income for Equity REITs comes from renting out these properties to tenants. Investors in Equity REITs can benefit from regular dividend payments and potential appreciation in property values.
Mortgage REITs
Mortgage REITs, also known as mREITs, do not own physical properties like Equity REITs. Instead, they provide financing for real estate purchases by purchasing or originating mortgages and mortgage-backed securities. Mortgage REITs earn income from the interest on these loans. While Mortgage REITs can offer higher dividend yields compared to Equity REITs, they are also more sensitive to interest rate changes and market conditions.
Hybrid REITs
Hybrid REITs combine characteristics of both Equity REITs and Mortgage REITs. They may own and operate real estate properties while also investing in mortgages or mortgage-backed securities. This diversification can help reduce risk and provide a more balanced income stream for investors. Hybrid REITs offer a mix of potential capital appreciation and dividend income.
Public vs. Private REITs
Publicly traded REITs are listed on stock exchanges and can be bought and sold by individual investors. Private REITs, on the other hand, are not traded on public exchanges and are typically only available to accredited investors. Public REITs offer liquidity and transparency, while private REITs may provide access to unique investment opportunities with potentially higher returns.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Investing in Equity REITs can provide stable income and potential for property appreciation, but they are subject to market risks and economic downturns. Mortgage REITs offer high dividend yields but are vulnerable to interest rate fluctuations. Hybrid REITs combine the benefits of both Equity and Mortgage REITs but may have a more complex investment structure. Public REITs offer liquidity and transparency, while private REITs may have higher return potential but limited liquidity.
Benefits of Investing in REITs
Investing in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) can offer a variety of advantages for investors looking to diversify their portfolios and generate income.
Steady Income Stream
REITs are required by law to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends. This can provide investors with a reliable and steady income stream, similar to rental income from owning physical real estate properties.
Potential for Capital Appreciation
In addition to regular dividend payments, REITs also have the potential for capital appreciation. As the value of the underlying real estate properties held by the REITs increases, so does the value of the shares, allowing investors to benefit from both income and capital gains.
Diversification in Investment Portfolio
Investing in REITs can offer diversification benefits to an investment portfolio. Real estate has a low correlation with other asset classes, such as stocks and bonds, meaning that adding REITs to a portfolio can help reduce overall risk and increase returns through diversification.
Liquidity and Accessibility
Unlike owning physical real estate properties, investing in REITs provides liquidity and accessibility to the real estate market. Investors can buy and sell REIT shares on major stock exchanges, making it easier to enter and exit positions compared to owning individual properties.
Professional Management
REITs are managed by professional teams with expertise in real estate acquisition, development, and management. This allows investors to benefit from the knowledge and experience of real estate professionals without having to actively manage properties themselves.
Risks Associated with REIT Investments
Investing in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) comes with certain risks that investors need to be aware of in order to make informed decisions. These risks can impact the performance of your investment portfolio and should be carefully considered before investing in REITs.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk is one of the key factors that can affect REIT investments. When interest rates rise, the value of REIT shares may decrease as investors seek higher returns from other investments. On the other hand, when interest rates fall, REITs may benefit from lower borrowing costs, potentially increasing their profitability.
Economic Downturns
During economic downturns, REITs may face challenges such as declining property values, increased vacancies, and lower rental income. This can lead to a decrease in dividends and share prices, affecting the overall performance of the investment. It is important for investors to consider the economic climate and its potential impact on REIT investments.
Strategies to Mitigate Risks
- Diversification: Investing in a variety of REITs across different sectors can help spread risk and reduce exposure to a single market segment.
- Research and Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on the REITs you are considering investing in, including their financial health, property holdings, and management team.
- Monitor Market Trends: Stay informed about market trends, economic indicators, and interest rate changes that could impact REIT investments.
- Long-Term Perspective: Consider investing in REITs with a long-term perspective, as short-term fluctuations may not accurately reflect the true value of the investment.
How to Invest in REITs
Investing in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) can be a great way to diversify your portfolio and potentially earn passive income. Here are some different methods available for investing in REITs and step-by-step guidance on how to start investing in them.
Opening a Brokerage Account
To begin investing in REITs, you’ll first need to open a brokerage account. This will allow you to buy and sell REIT shares just like you would with any other stock.
Choosing the Right REITs
Once you have your brokerage account set up, it’s important to research and choose the right REITs to invest in. Consider factors such as the type of real estate the REIT focuses on, its historical performance, and the management team behind it.
Investing in REIT Funds
Another method of investing in REITs is through REIT mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). These funds pool together money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of REITs, providing you with instant diversification.
Importance of Due Diligence
Before investing in any REIT, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research and due diligence. This includes analyzing the REIT’s financial statements, understanding its investment strategy, and evaluating its track record of performance.
Monitoring Your Investments
Once you’ve invested in REITs, it’s essential to regularly monitor your investments. Keep track of any news or updates related to the REITs you’ve invested in, and be prepared to adjust your portfolio if necessary.
Tax Implications of REIT Investments
Investing in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) can have specific tax implications that investors should be aware of in order to make informed decisions about their investments.
Tax Considerations for REIT Investors
- REITs are required by law to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends. These dividends are generally taxed at the investor’s ordinary income tax rate.
- Investors may also be subject to capital gains taxes when selling shares of a REIT, depending on how long they held the investment.
- One of the key tax advantages of investing in REITs is that they are not taxed at the corporate level, as long as they meet certain requirements set by the IRS.
Tax-Efficient Strategies for REIT Investments
- Investors can consider holding REITs in tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s to defer taxes on dividends and capital gains until withdrawals are made in retirement.
- Another tax-efficient strategy is to invest in REIT index funds or ETFs, which can provide diversification while minimizing the tax impact through lower turnover ratios.
- Investors can also take advantage of the 20% deduction on qualified REIT dividends available through the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, providing potential tax savings for eligible investors.
