Dive into the world of dividend stocks strategies where savvy investors harness the power of dividends to grow their portfolios. From selecting the right stocks to reinvesting dividends, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the world of dividend investing with confidence.
What are Dividend Stocks?
Dividend stocks are shares of a company that pay a portion of their earnings to shareholders in the form of dividends. These dividends are typically paid out regularly, either quarterly, semi-annually, or annually, providing a steady income stream for investors.
Examples of Well-Known Dividend-Paying Companies
- Johnson & Johnson: A healthcare giant that has a long history of paying consistent dividends.
- Procter & Gamble: A consumer goods company known for its strong dividend track record.
- AT&T: A telecommunications company that offers attractive dividend yields.
Benefits of Investing in Dividend Stocks
Investing in dividend stocks offers several advantages, including:
- Steady Income: Dividend payments provide a reliable source of income for investors, especially during market downturns.
- Long-Term Growth: Companies that pay dividends tend to be stable and established, offering the potential for long-term growth.
- Compound Returns: Reinvesting dividends can lead to the compounding effect, where returns generate additional gains over time.
Comparison of Dividend Stocks with Growth Stocks
While dividend stocks focus on providing regular income to investors, growth stocks prioritize capital appreciation. Here are some key differences between the two:
- Dividend Stocks: Prioritize income generation through regular dividend payments.
- Growth Stocks: Focus on reinvesting profits for future expansion and capital appreciation.
- Risk Profile: Dividend stocks are generally considered less risky due to the steady income stream, while growth stocks carry higher volatility but offer potential for greater returns.
Strategies for Selecting Dividend Stocks
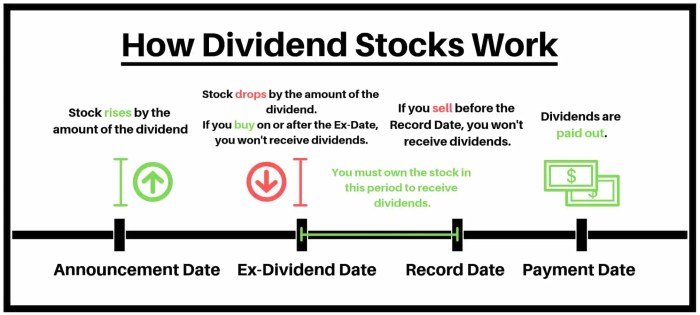
When it comes to choosing dividend stocks, there are several key criteria to consider in order to make informed decisions that align with your investment goals.
Importance of Dividend Yield
Dividend yield is a crucial metric that indicates the annual dividend payment as a percentage of the stock’s price. A higher dividend yield often signifies a better return on investment, but it’s essential to balance this with other factors like the company’s financial health and growth potential.
- Look for dividend yields that are sustainable and consistent over time.
- Compare the dividend yield of different stocks within the same industry to identify outliers.
- Consider the historical trend of dividend yield to assess the company’s dividend policy.
Evaluating a Company’s Dividend History
A company’s dividend history provides valuable insights into its financial stability and commitment to rewarding shareholders. Analyzing the consistency and growth of dividend payments can help you gauge the company’s reliability and long-term performance.
- Examine the number of years the company has been paying dividends without interruptions.
- Look for companies with a track record of increasing dividends regularly, indicating financial strength.
- Consider any cuts or suspensions in dividend payments, as they may signal underlying issues within the company.
Significance of Dividend Payout Ratio
The dividend payout ratio is a key indicator of a company’s financial health and sustainability of dividend payments. It measures the proportion of earnings distributed as dividends, showing how much of the company’s profits are allocated to shareholders.
- A lower dividend payout ratio suggests that the company retains more earnings for growth and potential dividend increases.
- High dividend payout ratios may indicate that the company is distributing a significant portion of its earnings, potentially limiting future growth opportunities.
- Balance the dividend payout ratio with other financial metrics to get a comprehensive view of the company’s dividend policy.
Reinvesting Dividends
When it comes to investing in dividend stocks, one strategy that can significantly boost your returns over time is reinvesting dividends. By reinvesting the dividends you receive from your investments back into buying more shares of the same stock, you can take advantage of compounding returns and accelerate the growth of your wealth.
Advantages of Reinvesting Dividends
- Compound Returns: Reinvesting dividends allows you to earn returns not just on your initial investment, but also on the dividends you receive. Over time, this compounding effect can lead to exponential growth in your investment.
- Cost Averaging: Reinvesting dividends helps you buy more shares when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high. This dollar-cost averaging strategy can help reduce the impact of market volatility on your portfolio.
- Increased Income: As you reinvest dividends and buy more shares, your future dividend payments will also increase. This can create a snowball effect, leading to higher income streams in the long run.
Methods of Reinvesting Dividends
- DRIP (Dividend Reinvestment Plans): Many companies offer DRIP programs that allow you to automatically reinvest your dividends in additional shares of the same stock without paying commission fees. This is a convenient and hassle-free way to reinvest dividends.
- Manual Reinvestment: If your brokerage account does not offer DRIP, you can still manually reinvest your dividends by using the cash dividends to purchase more shares of the stock. This gives you more control over the reinvestment process.
Accelerating Wealth Growth with Reinvesting Dividends
Reinvesting dividends can have a significant impact on the growth of your investment portfolio. For example, let’s say you invest $10,000 in a dividend stock with a 4% dividend yield. If you reinvest the dividends over 20 years, assuming a 7% annual return, your investment could grow to over $32,000. However, if you do not reinvest the dividends and instead take them as cash, your investment would only grow to around $21,000. This example illustrates how reinvesting dividends can accelerate wealth growth over time.
Risks and Challenges of Dividend Stocks
Investing in dividend stocks comes with its own set of risks and challenges that investors need to be aware of. These risks can impact the overall performance of a dividend stock portfolio and potentially affect the income generated from dividend payments.
Potential Risks Associated with Investing in Dividend Stocks
- Market Volatility: Stock prices can fluctuate, affecting the value of dividend stocks.
- Interest Rate Risk: Changes in interest rates can impact the attractiveness of dividend stocks compared to other investments.
- Company Performance: Poor company performance can lead to reduced or suspended dividend payments.
- Regulatory Risks: Changes in regulations can affect dividend policies and payments.
Economic Factors Impacting Dividend Payments
- Economic Downturns: During recessions, companies may struggle to maintain dividend payments.
- Inflation: High inflation rates can erode the purchasing power of dividend payments over time.
- Currency Fluctuations: Changes in exchange rates can impact the value of dividend payments for international stocks.
Concept of Dividend Cuts and Implications
Dividend cuts occur when a company reduces or eliminates dividend payments to shareholders.
- Impact on Share Price: Dividend cuts can lead to a decrease in the stock price as investors react to the reduced income.
- Loss of Investor Confidence: Dividend cuts may signal financial instability or poor performance, leading to a loss of investor trust.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks
- Diversification: Spread investments across different sectors and industries to reduce risk exposure.
- Research and Due Diligence: Thoroughly analyze company financials and dividend history before investing.
- Monitor Portfolio: Stay informed about economic conditions and company performance to make timely adjustments.
- Consider Total Return: Focus on the total return of a stock (dividends plus capital appreciation) rather than just the dividend yield.
